Intro and Terms
In this chapter main @bluepjs terms will be introduced without deep details.
@bluepjs consists of two main parts:
Virtual Machine (VM)
VM designed to execute Blueprints
npm install @bleupjs/vm
VM can be used both in browser and nodejs side in same way.
Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
IDE designed to manage Blueprints and Libraries
npm install @bleupjs/vue3-ide
Note
Ok, to be precise in terminology this is not “REAL IDE” - this is more “editor” right now.
“Full IDE” should also include “execution/debugging environment” and this part will be fully implemented later.
Note
Currently IDE build with Vue3 and provided as Vue3 module.
vite/nuxt/pure/react/etc version will be developed later.
Both parts are independent packages, so can be used as needed.
Other terms, used in code and this documentation are:
Application (App)
@bluepjs is not a standalone software, but a scripting engine.
It’s designed to be included into other applications as scripting engine for applications entities.
In this documentation developed application, used @bluepjs engine named Application (or App)
Developer
Person (or group of people) who develops Application, Modules or Libraries
User
Person (or group of people) who use @bluepjs IDE to develop Application behavior
Module
@bluepjs designed to be expandable with 3-rd party code organized into special Modules.
Modules are designed to be imported/exported by programmers (Developers) and may contain new Nodes, Libraries, Events, Actors and other entities to expand and organize @bluepjs functionaly and can be universal or App specific.
Libraries (Libs)
Blueprints are stored and organized in Libraries.
@bluepjs doesn’t care about storing Libraries - this part should be done by Application - Library structure is JSON compatible and can be easy stored in different ways.
Libraries designed to be imported/exported by regular users as fiendly reusable modules and store all required reusable module content and scripts.
Note
Right now only single “Default” library is supported
Full support (use/import/export) will be added in next versions
Actors
Application entities controlled by VM in @bluepjs named Actors.
They are developed by Developer and are Application, Library or Module specific.
Actors may have:
State - readonly Actor properties.
Methods - actions to be executed by Actor.
Events - actions to be fired from Actor and managed by VM
Events
VM designed to manage events from Actors (Actor event) and from Modules (also named in documentation as Global Event or VM Event).
Events may have Outputs to transmit event data into Blueprint.
Global Events may have Configuration fields for specific tuning.
Note
In this documentation term Event without specification to “Actor”, “Global” or “VM” should be specified by context.
Blueprints
Library scriptable entities. Can be:
Library Function script
Library Class Method script
Library Event script
Blueprints are constructed with Nodes and Edges into Execution Flow in IDE
Nodes
Nodes are minimal Blueprint scripting block. They can represent Java Script code provided by Developers or other Libraries Blueprints.
Nodes has Inputs and Outputs and may be two different types:
Executable Nodes
This Nodes has special Executable Input and at least one Executable Output for Execution Flow
For example:
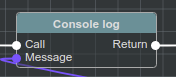
Note
Executable Nodes are easy recognized by having header
Modifier Nodes
modifiers - this Nodes doesn’t have Executable Inputs or Executable Outputs and Execution Flow of this Nodes depends on Edges
For example:
Getter Nodes
getters - this Nodes, same as modifiers doesn’t have Executable Slots. Also, they don’t have Input slots and have only Output slots (regulary - one).
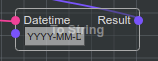
Slots (Node Slots)
Slot in this documentation is a common name for any Node Input or Output, so there are Input Slots and Output Slots
Slot color and shape visually represents slot data type.
Slots can be connected o disconnected, for example:
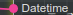
Connected Input Slot of type basic/datetime named “Datetime”
Disconnected Input Slot of type basic/string with manual value “Cron at “
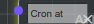
Disconnected Input Slots values may be inputed manually
Edges (Connections)
Nodes connected together with Edges by Slots.
Edge color represents data type of connected Slots
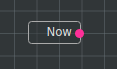
For example - Edge of type basic/datetime connecting Output Slot named “Now” with Input Slot named “Datetime”
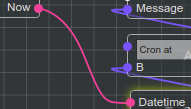
Execution Flow
Way of Nodes ordering for execution defined by connecting Nodes with Execution Slots
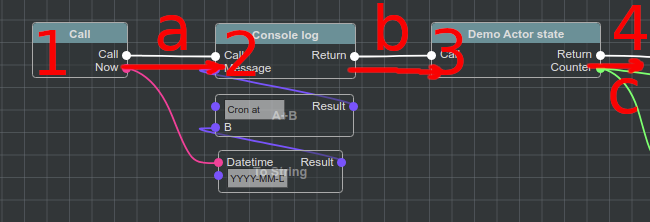
On example image Execution Edges are a, b and c and they define Nodes execution order.
Deeper information about Execution Flow will be covered in next chapter.